
When standing up, however, nerve signaling traffic in the autonomic ganglion increases, so the researchers theorized that a drug that affected the autonomic ganglion would improve orthostatic hypotension patients' standing blood pressure but not increase the blood pressure while lying down.Īfter a small, open trial of 15 subjects in which the pyridostigmine performed effectively as hoped, the investigators proceeded to the current double-blinded study of 58 patients. Pyridostigmine works at the level of the autonomic ganglion, which has minimal nerve signaling traffic when lying down. "We wanted a 'smart drug' that would only increase blood pressure when standing up, and not when lying down," says Dr. Low felt that this price was too high, and that treating with medications that raised blood pressure while standing but raised blood pressure while lying down amounted to trading one problem for another. Thus, the drugs would work for patients with orthostatic hypotension when they stood up, but their blood pressure would be too high when lying down, increasing their risk of stroke. Low, is that most medications that increase blood pressure raise blood pressure in all positions. The challenge with trying to fix this condition, according to Dr.
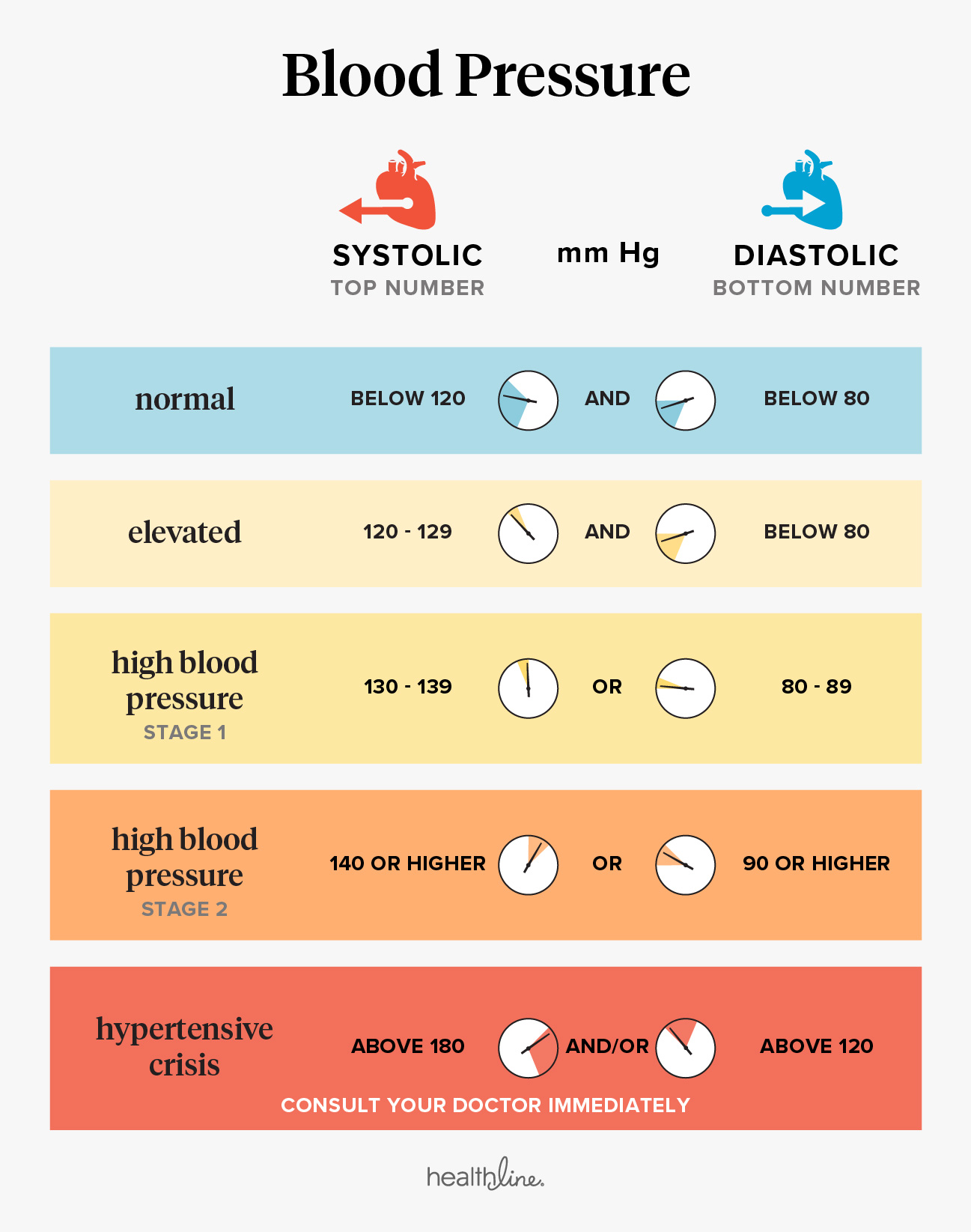
Studies conducted at Mayo Clinic by Peter Dyck, M.D., neurologist, indicate 10 percent of diabetics have orthostatic hypotension. Certain drugs, such as diuretics and medication used to control blood pressure, are also common catalysts for the condition. Common causes of orthostatic hypotension include diabetes, autonomic neuropathy, multiple system atrophy, pure autonomic failure and Parkinson's disease. In general, blood pressure control lessens as one ages, according to Dr. Orthostatic hypotension is especially common in those over age 70. Low's study, one-third were able to stop taking any other orthostatic hypotension medications, and others were able to lower the amount of other drugs needed. Low hypothesized that it would also improve nerve cell transmission for orthostatic hypotension patients and trigger the reflex that controls blood pressure in all positions. The drug, pyridostigmine, has been used for years for myasthenia gravis, a neuromuscular transmission disorder. "This would be a good drug to provide the first line of treatment." "This is a significant step forward for these patients," says Phillip Low, M.D., Mayo Clinic neurologist and lead study investigator. Mayo Clinic neurologists have discovered a drug application smart enough to alleviate orthostatic hypotension - problems with sinking blood pressure when standing up from a sitting position - without the unwanted effect of also causing patients' blood pressure to soar when lying down. If your blood pressure isn't normal, a healthy lifestyle - oftentimes along with medication - can help bring it under control and reduce your risk of life-threatening complications.ROCHESTER, Minn. If your blood pressure is normal, maintaining or adopting a healthy lifestyle can prevent or delay the onset of high blood pressure or other health problems. If you're a healthy adult age 65 or older, your treatment goal is also less than 130/80 mm Hg. If you are an adult with a 10 percent or higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease in the next 10 years, or if you have chronic kidney disease, diabetes or coronary artery disease, your treatment goal is less than 130/80 mm Hg. Talk to your doctor about taking more than one medication. Stage 2 high blood pressure (hypertension) Talk to your doctor about taking one or more medications. Stage 1 high blood pressure (hypertension) If you also have heart disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease or certain other conditions, you may need to treat your blood pressure more aggressively. †These recommendations address high blood pressure as a single health condition.

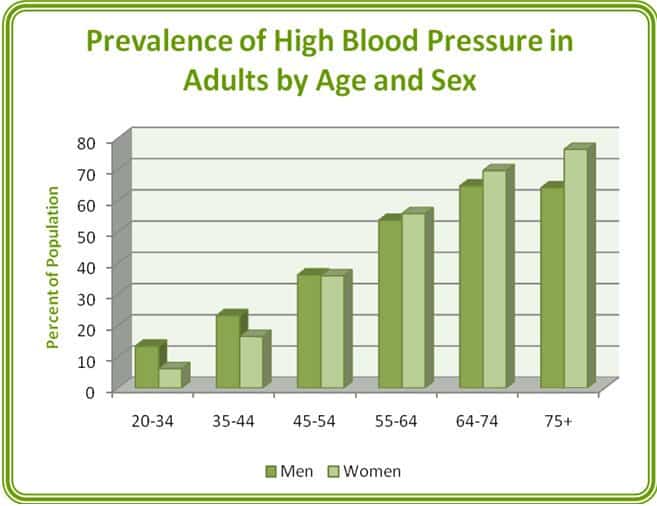
Talk to your child's doctor if you're concerned your child has high blood pressure. *Ranges may be lower for children and teenagers. For example, if your blood pressure reading is 125/85 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg), you have stage 1 hypertension. If your systolic and diastolic readings fall into two different categories, your correct blood pressure category is the higher category. Here's a look at the four blood pressure categories and what they mean for you. To get an accurate blood pressure measurement, your doctor should evaluate your readings based on the average of two or more blood pressure readings at three or more office visits. The level of your blood pressure determines what kind of treatment you may need. Blood pressure readings fall into four general categories, ranging from normal to stage 2 high blood pressure (hypertension).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
